LED 101: What Is LED Lighting Made Of
What Are LED Light Bulbs?
The LED abbreviation stands for Light Emitting Diode. An LED light bulb produces illumination through these diodes, as opposed to the filament and gas contained in incandescent and other older bulb types.
To help you better understand the cost-saving and environmental advantages of LED vs incandescent bulbs, the pros at TCP break down what LED lighting is made of, how LEDs work, and the many benefits of switching to LED lights.
How LED Light Bulbs Work and Why They’re Revolutionizing Lighting
An LED light bulb is a solid-state lighting (SSL) device. That means it contains no gasses — unlike incandescent and fluorescent bulbs, which contain argon gas. This gas-free construction makes LED bulbs safer and more efficient in producing illumination.
Instead of heating a filament with an electrical current until it’s hot enough to glow with light the way incandescent bulbs do, LED technology passes energy through a semiconductor to produce light. The semiconductor is typically a solid chemical agent or compound that can conduct electricity, embedded in a circuit board. An LED light is formed when bringing P-Type (+) and N-Type (-) semiconductors together that form a PN Junction. LEDS are considered more environmentally friendly lights because they contain none of the harmful substances found in other lighting types, like lead and mercury. Most LED lights are designed to run on low voltage (12-24V), but many can run on higher voltages (120-277V).
The illumination from an LED bulb shines in only one direction whereas CFLs and incandescents put out heat and light in all directions. This “directional” light source is part of what makes LEDs more energy efficient and appropriate for a variety of applications. They can be configured to produce a rainbow of colored light, as well as a wide range of white lighting color temperatures, measured in Kelvins from warmest candlelight (2000K) to neutral white (3500K) to the coolest bluish white (5000K+).
What Are LED Lights Made Of?
An LED light bulb is complicated technology. TCP has been on the forefront of LED innovation for more than 30 years, and we have deep expertise in every step of the LED production process from initial design through global distribution.
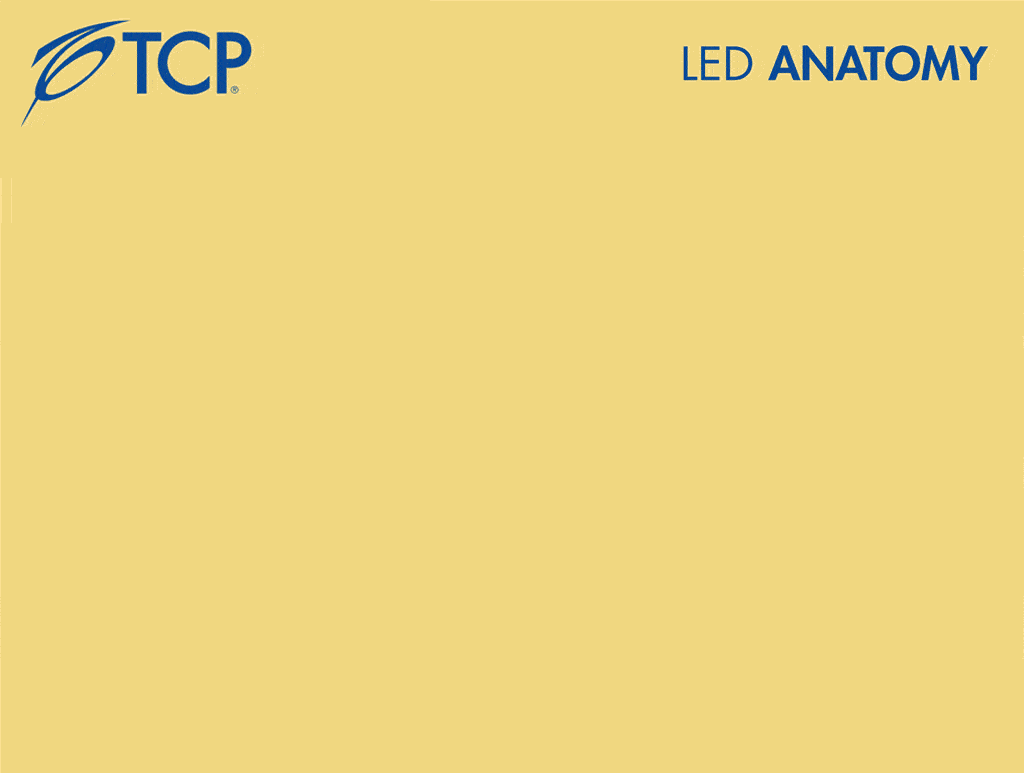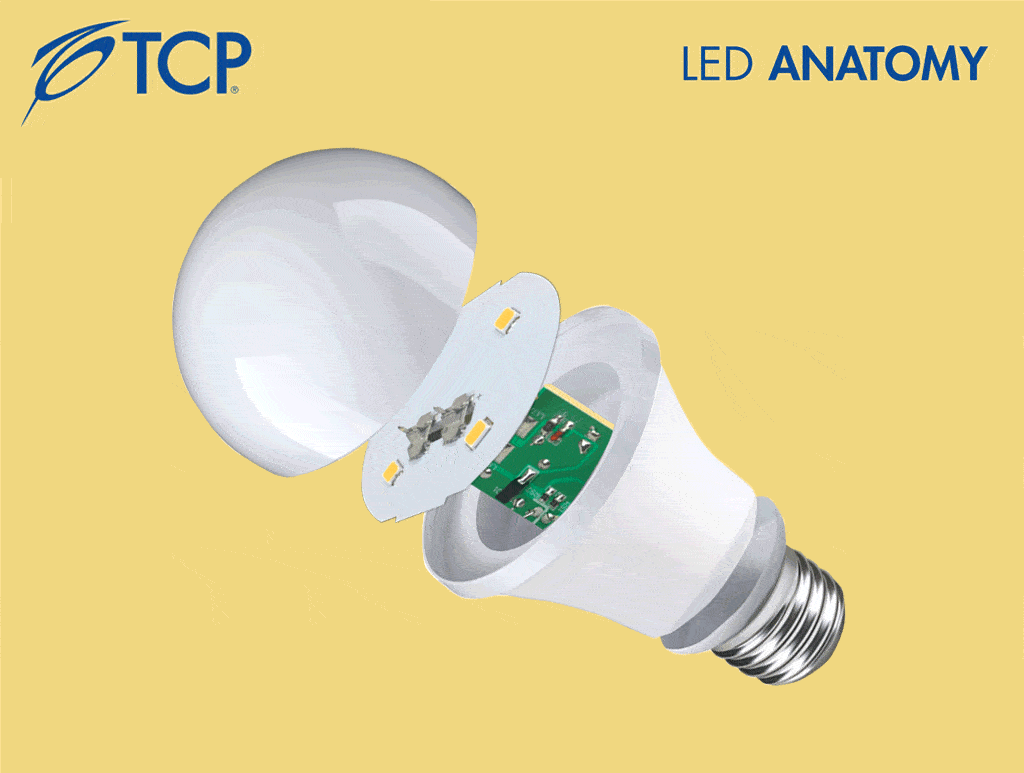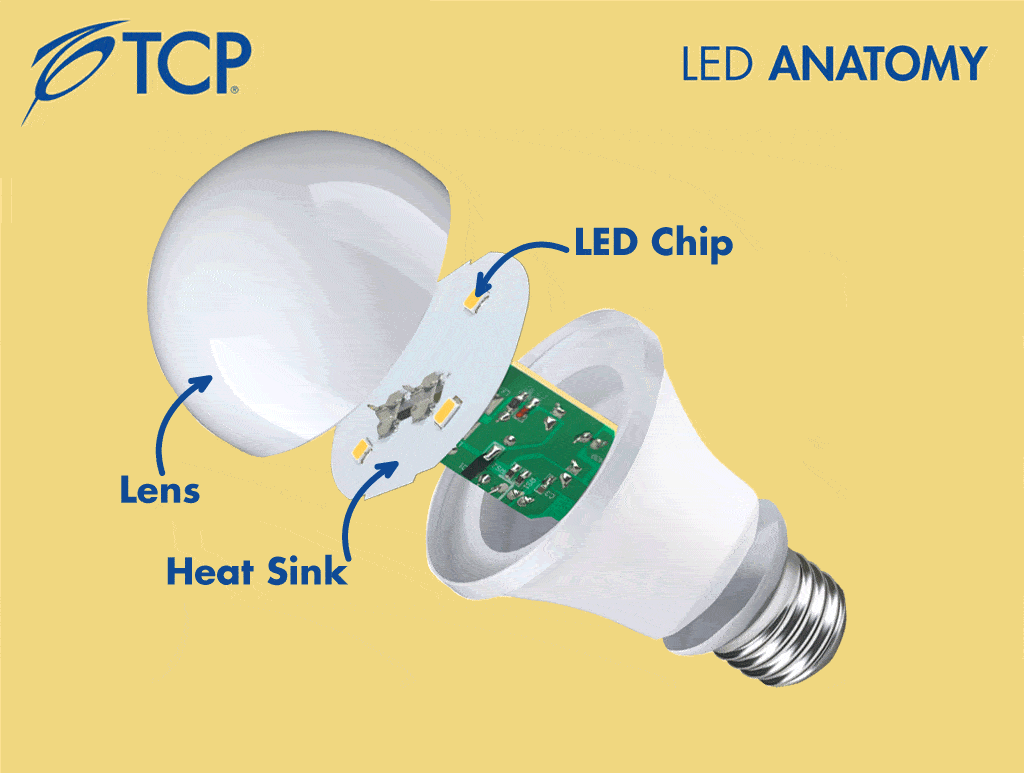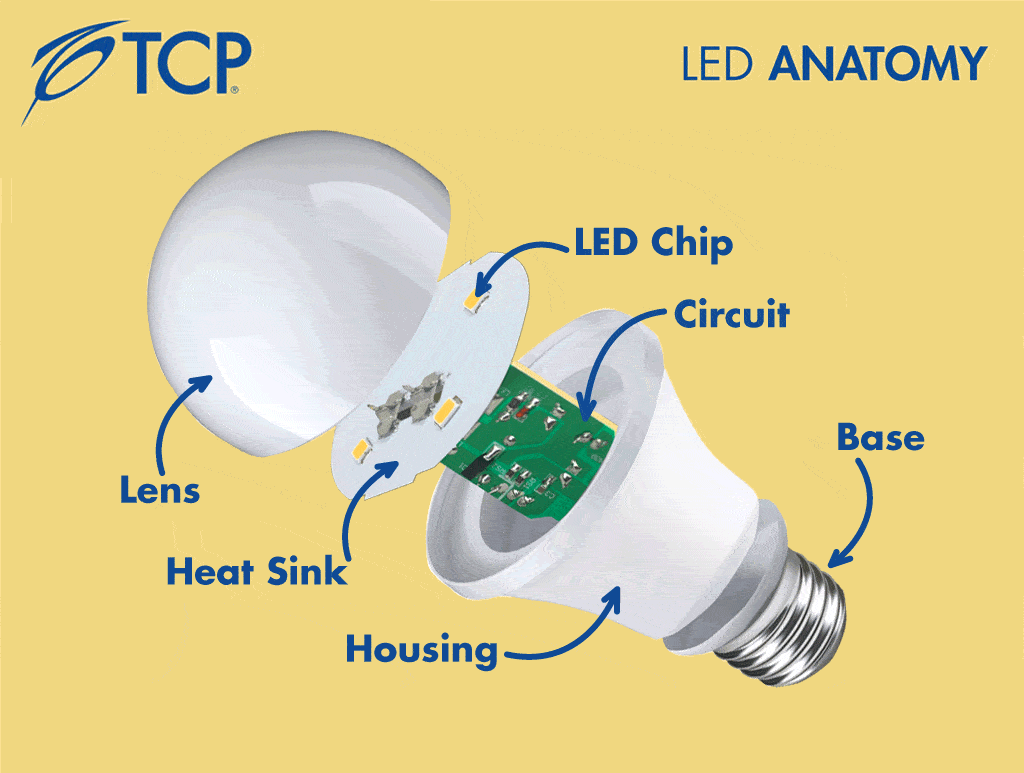
To help make LED technology more accessible, we explain the various components of an LED light bulb, which include:
- LED Chips
- Heat Sink
- Circuit Board/Driver
- Housing
- Base
- Lens/Optics
1. LED Chips
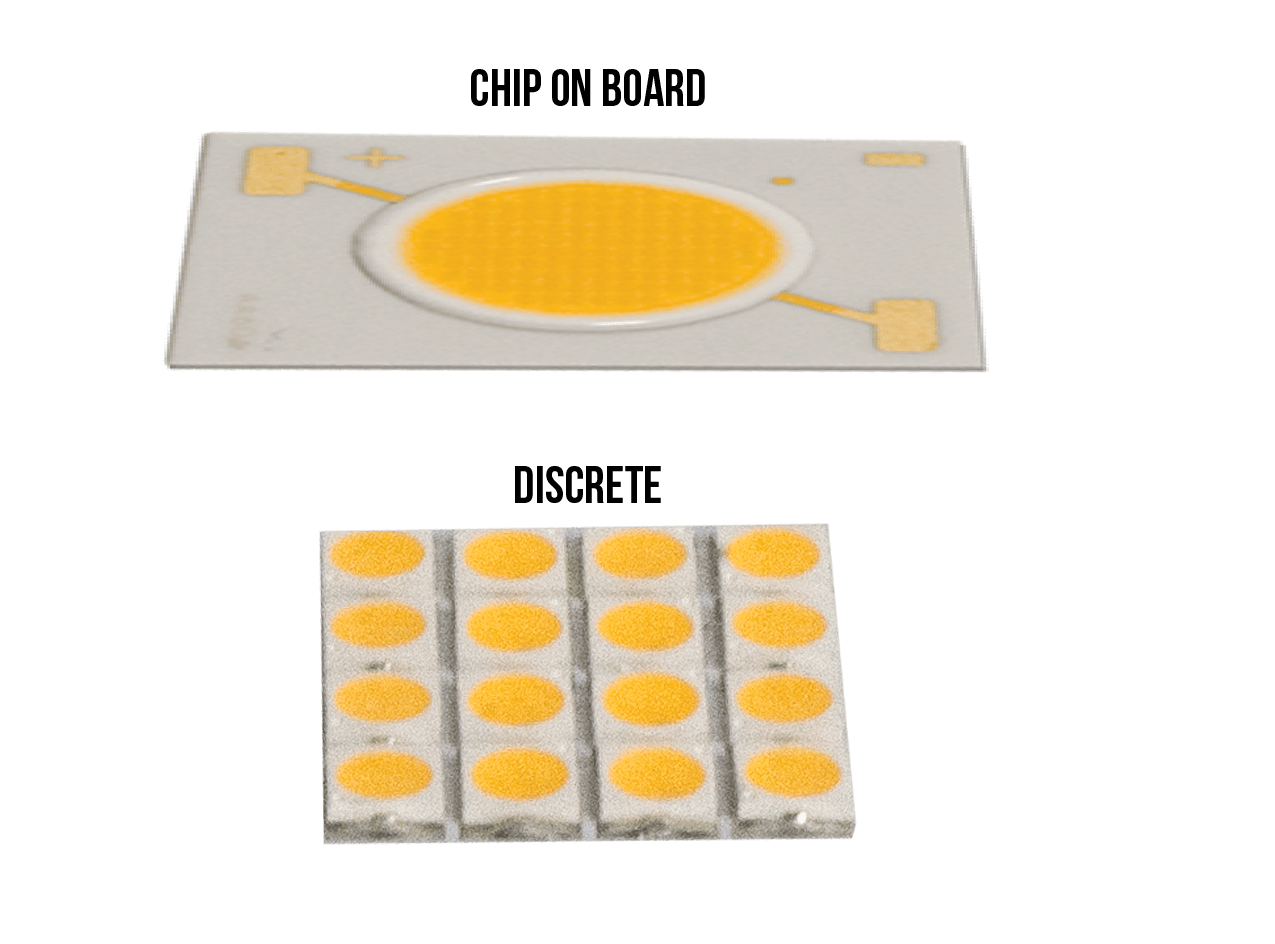
LED chips do the heavy lifting of creating light. They look like small yellow circles attached to a piece of metal, also known as a printed circuit board or PCB. TCP engineers use two main types of chip configurations:
- Chip on Board (COB): a single LED chip on PCB that creates a clean, uniform beam pattern
- Discrete: multiple LED chips placed on PCB to achieve a desired lumen (brightness) output
2. Heat Sink
All light sources produce heat. Older bulbs radiated heat into their immediate environment, making the bulb hot to the touch. In LED bulbs, a heat sink conducts the heat away from the light emitting diodes to keep the entire unit cool. The heat sink is composed of a piece of metal the LED chip sits on that provides a path for heat to leave the light source.
3. Circuit Board/Driver
The terms circuit board and driver are generally interchangeable and refer to the “brain” of the bulb. This component takes energy from the electrical socket and tells the LEDs what function to perform, like turning on and off, dimming or changing color. LED drivers are similar to ballasts in fluorescent lamps. They also protect LED bulbs from voltage or current fluctuations, which could damage the unit.
4. Housing
The circuit board of an LED heats up when energy passes through it, creating the necessity for a heat-conducting component. A housing made of material with high thermal conductivity, typically aluminum, makes up the lower section of the bulb where it connects to the base. This housing absorbs the heat from the circuit board, so it will become warm to the touch — but not as hot as halogen, incandescent or fluorescent lighting.
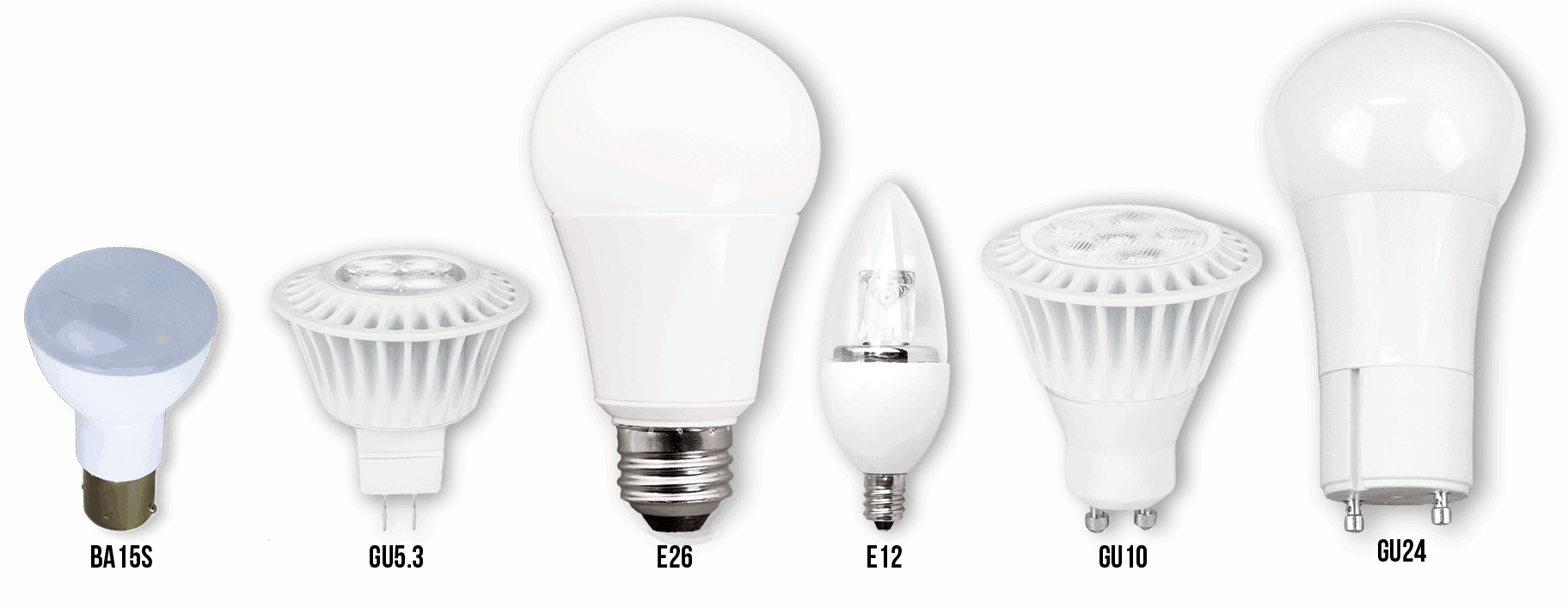
5. Base
The base of a light bulb is the part that screws into a fixture or socket. Because LEDs are designed as direct replacements for existing light bulbs, they are available in a wide selection of base types, including all those you recognize from more traditional bulbs. There are many types of LED lamp bases:

6. Lens/Optics
Due to the brightness of LEDs, a covering component is added to evenly distribute the light. This cover is called a lens on single-direction lamps and optics on omni-directional lamps. These components are typically made of shatter-resistant plastic and help give LEDs the familiar look and feel of more traditional bulbs.
LED vs Incandescent Bulbs: What’s the Advantage?
The federal ban on incandescent light bulb manufacturing and California’s recent ban on CFLs have brought about a lot of confusion. Understanding the cost-saving and environmental benefits of LEDs can help demystify the process of choosing the best replacements for older lighting sources.
The benefits of switching to LED lights include:
- Lower energy use – LED bulbs consume up to 90% less energy than older bulb types while producing equally brilliant illumination, putting less stress on utility providers and our limited natural resources.
- Less frequent replacements – Incandescent bulbs tend to burn out after about one year of use whereas LEDS have lifespans of up to 20 years.
- Lower utility bills – Because LED bulbs do not heat up the way incandescents do, they won’t raise the ambient interior temperature as much, translating to lower costs for maintaining a comfortable indoor atmosphere.
- No need for new fixtures – LED light bulbs are designed as incandescent lighting alternatives, so they’re made with bases that fit in most existing fixtures for an easier transition.
Where Can You Use LED Bulbs?
You can use LED light bulbs anywhere you previously used incandescents, CFLs, fluorescents or other traditional bulbs — as well as some locations that were unsuitable for the high heat output of older lighting.
From pendants, recessed lighting and other home lighting trends to office ceiling panels, far-red horticultural options and more lighting options to level up your business, the possibilities for high-quality, versatile LED light bulbs are nearly endless.
The innovators at TCP have even designed multi-tasking LED lighting that kills germs while delivering daylight-caliber illumination for healthier homes and workplaces. Find colored LED bulbs for every season, high CRI options for superior color rendering, industrial LED lighting choices, outdoor LED bulbs and more.
Embrace a Bright Future With LED Lighting Technology
TCP is committed to leading the lighting industry toward a brighter, greener future. Join us in illuminating your world with the versatility, energy efficiency and brilliance of LED lighting. Browse our product offerings and reach out for our expert help with anything from pricing your commercial project to understanding residential warranties to finding rebates and tax rebates on LED lighting.
Related Articles
Enhancing Retail Spaces with LED Lighting Solutions
Effective retail lighting is essential for attracting and retaining customers, as it influences customer behavior, mood, and overall shopping experience. The Impact of Light Design on Customer Behavior Lighting plays a pivotal role in shaping how customers interact...
Lighting Maintenance in Industrial Facilities
Managing a warehouse facility is more than just keeping shelves organized. The lighting that constantly surrounds the people and products play a big part in the well-being of the business. Lighting maintenance in industrial facilities helps ensure safety, reduce...
Improve Learning Environments with LED Lighting Solutions
Creating an optimal learning environment requires more than just desks and whiteboards – lighting plays a crucial role in shaping students' focus, energy levels and overall well-being. Schools that insist on high-quality LED lighting solutions can enhance student...